Fibroid is a non-cancerous growth in the uterus that can develop during a women’s childbearing years.
The cause of fibroid isn’t well understood.
Risk factor include:
- Family history of fibroids
- Obesity
- Early onset of Puberty (Hormones Estrogen and Progesterone appear to promote growth of fibroids).
Symptoms include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Prolonged period and pelvic pain
- Frequent urination
- In some cases there are no symptoms.
A little about fibroid:
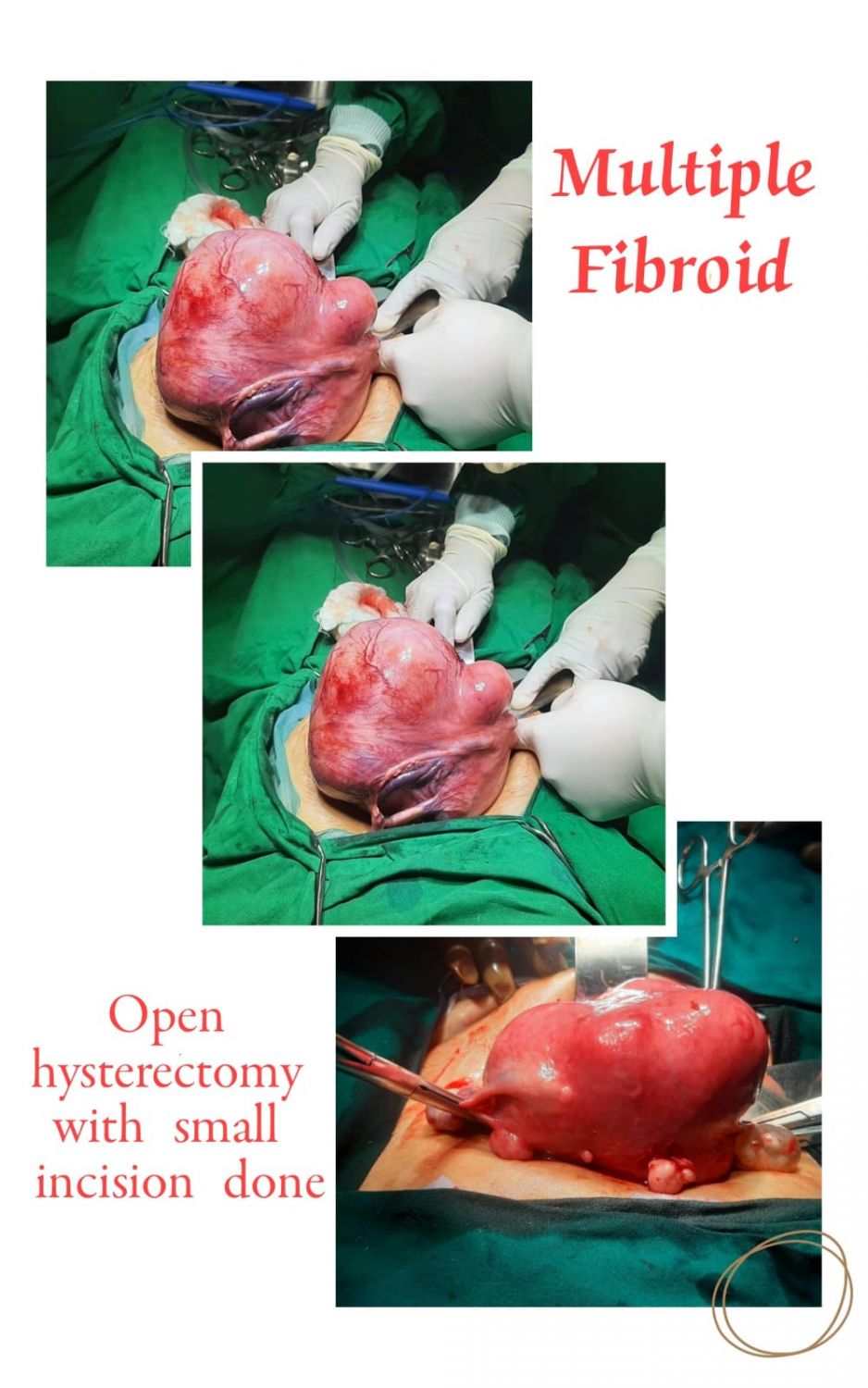
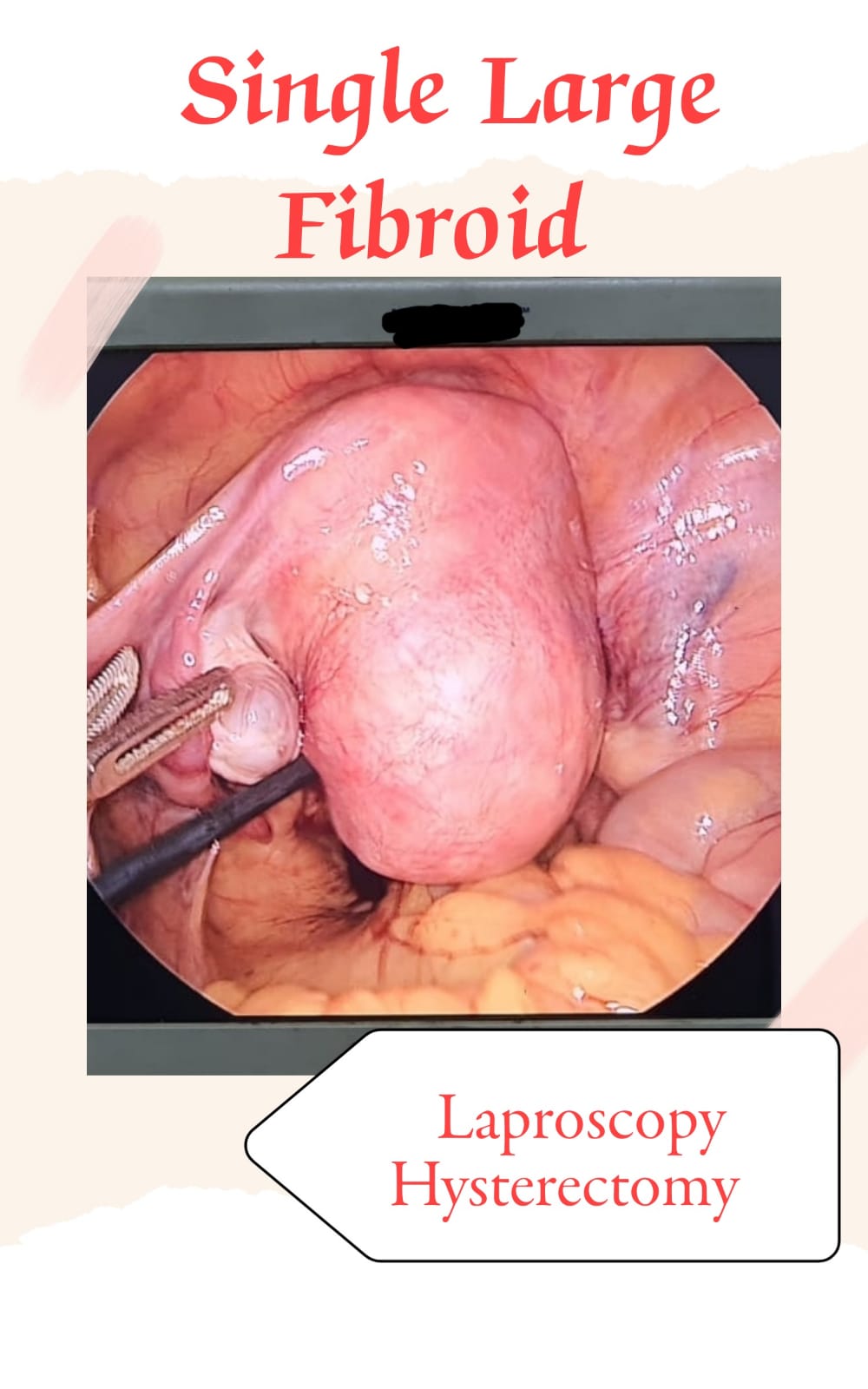
- Fibroids if left untreated can grow and continue to grow both in size and number.
- Fibroids are almost always benign (non-cancerous), Rarely less than 1 in 1000 a cancerous fibroid will occur, This is called leiomyosarcoma.
- Fibroids typically grows slowly or not at all.
- In many cases they shrink on their own, especially after menopause.
- You may not need a treatment unless you’re bothered by symptoms.
- Many women who have fibroids can get pregnant naturally.
- In some cases fibroids can impact your fertility.
- To know if your fibroids are growing is when you experience an increase in symptoms such as heavier bleeding or more pain than usual.
- To detect fibroids we do ultrasound and if required MRI pelvis.
Can Fibroids Turn Into Cancer?
Fibroids are 99.99% benign.
What are the Benefits of Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
- It is an effective alternative to hormonal treatment & surgery
- Minimal hospital stay
- Completely non-invasive – no surgery and no blood loss
- Preserves the uterus, cervix and ovaries
- improvement in your quality of life
- Significant decrease in menstrual bleeding from symptomatic fibroids
- Quick return to normal activities
How Do I know For Sure That I Have Fibroids?
- Following are the methods:
- Pelvic examination
- PAP smear
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
- Hysterosonogram
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
Who are at Risk for Uterine Fibroids?
- Following are the factors
- Family history.
- Age
- Obesity.
- Eating habits
- Ethnic origin
What are the treatment options for fibroids?
- Supportive care-Monitoring for changes or improvement.
- Devices- Progestin IUD
- Medication- Birth control, Hormones, Suppressants.
- Medical Procedure- Uterine Artery Embolization.
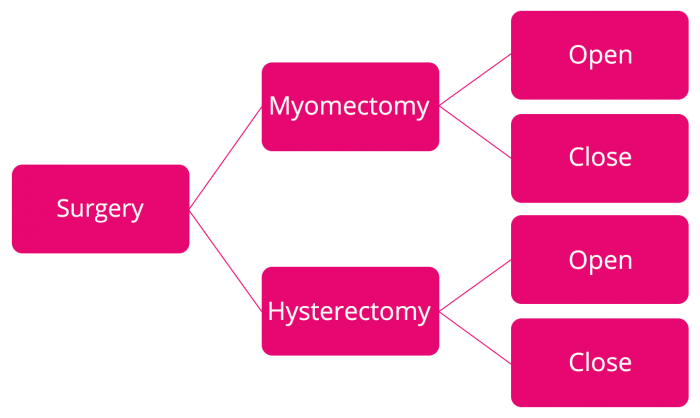
- Surgery